Embark on the Wonderful Journey of Indoor Hydroponic Sweet Pepper Cultivation
Imagine, within your own home, cultivating brightly colored and delicious-tasting sweet peppers, unhindered by weather and seasonal limitations. This is no longer an unattainable dream, but a reality easily achieved through hydroponic technology. Hydroponics, an innovative soilless cultivation method, uses nutrient solutions instead of soil to provide essential nutrients and water to plants. This method not only saves space but also effectively reduces pests and diseases, making indoor cultivation a simple and efficient choice.
This guide will detail how to cultivate sweet peppers indoors using a hydroponic system. It includes the Deep Water Culture (DWC) system, a simple yet efficient hydroponic technique suitable for both beginners and experienced gardening enthusiasts. From selecting seeds to harvesting mature sweet peppers, complete the entire process step-by-step and enjoy fresh, healthy homegrown vegetables at home.
Quick Guide: 6 Steps to Easily Grow Hydroponic Bell Peppers Indoors
Prepare the Hydroponic System and Planting Space
Choose a suitable indoor location, ensuring there is enough light (natural or artificial). Prepare a basic hydroponic system, such as a Deep Water Culture (DWC) system, which includes a hydroponic container, water pump, and nutrient solution.
Selecting the Right Sweet Pepper Seeds
Choose high-quality sweet pepper seeds. Consider selecting varieties suitable for indoor growth, which are typically more adapted to space and light requirements.
Sweet Pepper Seed Germination
Sow the seeds on a moist germination pad or sponge, maintaining proper humidity and temperature to promote germination. Once the seeds have sprouted, transplant the seedlings into the hydroponic system.
Managing Nutrient Solution and Water Quality
Regularly check and adjust the pH and electrical conductivity of the nutrient solution to ensure plants receive appropriate nutrition. Also, keep the water clean to prevent the growth of algae and bacteria.
Light and Temperature Control
Ensure the sweet peppers receive sufficient light, about 14-16 hours of light per day. Maintain indoor temperatures between 18°C and 25°C to promote good growth.
Monitoring and Harvesting
Regularly check the growth of the plants, paying attention to any signs of pests or diseases. Once the sweet peppers are mature, they can be carefully picked directly from the plant.
About hydroponic Bell Peppers

Nutritional Value of Sweet Peppers
- Sweet peppers, known for their vibrant colors and unique flavor, are also a highly nutritious vegetable. They are rich in a variety of vitamins and minerals, offering numerous health benefits. Here are some key nutritional facts:
- Rich in Vitamin C: Sweet peppers are an excellent source of vitamin C. A medium-sized red sweet pepper can provide over 200% of the recommended daily intake. Vitamin C is a powerful antioxidant, which helps strengthen the immune system and promote skin health.
- Contains Various B Vitamins: Sweet peppers contain B vitamins, including vitamin B6 and folate, which are beneficial for the health of the nervous system and the formation of new cells.
- Rich in Antioxidants: In addition to vitamin C, sweet peppers contain other antioxidants such as vitamin A, E, and various flavonoids. These antioxidants help combat free radicals, reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
- Low in Calories and High in Fiber: Sweet peppers are low in calories and high in fiber, which aids in digestive health and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Mineral Content: Sweet peppers also contain minerals like potassium, iron, and magnesium, which are crucial for heart health, blood circulation, and muscle function.
What are hydroponics growing systems?

Hydroponic cultivation, as a highly efficient soilless farming method, offers various systems on the market, each with its unique features and advantages:
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT):
In this system, plant roots are exposed in a slender channel where nutrient solution continuously flows over the roots, providing essential moisture and nutrients. This system is suitable for fast-growing plants with smaller root systems.
Ebb and Flow System:
This method involves periodically pumping the nutrient solution from a reservoir to a plant growing tray, then draining back into the reservoir. It is suitable for a variety of plants, especially those that require periodic drying of the roots.
Drip System:
This system supplies nutrient solution directly to the plant roots through small drippers, suitable for plants that need precise control of moisture and nutrients.
Aeroponics:
In this method, plants are suspended in air, with their roots surrounded by a fine mist. This provides a high supply of oxygen, promoting rapid growth.
Deep Water Culture (DWC):
As a simple and efficient hydroponic method, the DWC system places plants in a container filled with nutrient solution, with the roots directly immersed in the nutrient solution. This system is particularly suitable for beginners, as it does not require complex timing systems or frequent maintenance. It is very suitable for growing plants like sweet peppers.
How to set up an indoor hydroponic growing system?
To DIY an indoor Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponic system, you need to prepare the following basic components and materials. This system is simple to set up and very suitable for beginners.
DIY Deep Water Culture (DWC) Hydroponic System Checklist:
- Container:
Choose a sufficiently deep container, such as a plastic storage bin or a dedicated hydroponic container, to hold the nutrient solution.
- Net Pots:
These pots will be placed at the top of the container to hold the plants and the growing medium.
- Growing Medium:
Such as rockwool, perlite, or clay pebbles, used to support the plant and maintain moisture around the roots.
- Air Pump or Water Pump:
An air pump is used to supply oxygen to the nutrient solution, and an air stone helps disperse the bubbles, ensuring the roots receive ample oxygen.
- Nutrient Solution:
Choose a hydroponic nutrient solution suitable for the growth of sweet peppers.
- pH Testing Kit:
For testing and adjusting the pH of the nutrient solution to ensure it is within the ideal range for plant growth.
- Water Level Indicator (optional):
To help monitor the water level inside the container.
- LED Grow Light:
If indoor lighting is insufficient, use an LED grow light to provide the necessary light.
Assembly Steps:
- Prepare the Container:
Cut appropriate-sized holes in the lid of the container for placing the net pots.
- Install Air Pump and Air Stone:
Connect the air stone to the air pump and place it at the bottom of the container.
- Add Nutrient Solution and Water:
Mix the nutrient solution with water according to the instructions and pour it into the container until the appropriate water level is reached.
- Adjust pH Level:
Use the pH testing kit to test the pH of the nutrient solution and make necessary adjustments.
- Place the Plants:
Put the plants along with the growing medium into the net pots, ensuring the roots can reach the nutrient solution.
- Set Up Lighting:
Adjust the position and lighting time of the LED grow light according to the needs of the plants.
However, I understand that preparing all of this can be challenging for beginners, and you also need to acquire specialized knowledge. Fortunately, many new intelligent hydroponic growing systems are available, making starting your indoor hydroponic garden easier.

If you're interested, try the LetPot Hydroponics Growing System, which features innovative automatic watering and nutrient functions and integration with an app. With these features, you can effortlessly begin hydroponic cultivation, even if you're a novice gardener.
Learn about LetPot® and customer stories:
- Growing Cherry Tomatoes Indoors: A Personal Tale of Juicy Rewards
- Enjoy Growing Cherry Tomatoes At Home - LetPot Indoor Hydroponic System
How to grow hydroponic bell peppers indoors? (Step-by-step guide)
Step 1: Choose a hydroponic bell peppers
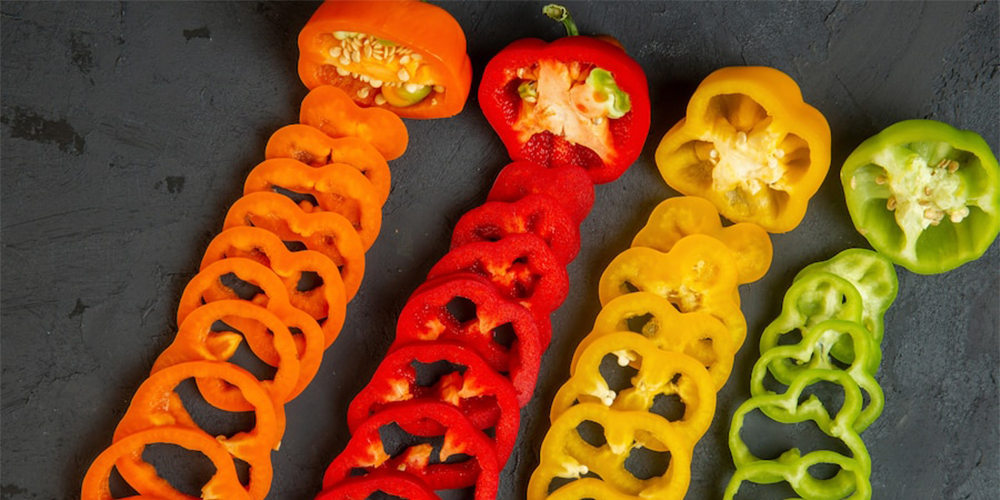

Bell Peppers
Characteristics: These are the most common type of sweet peppers and come in a variety of colors including green, red, yellow, orange, and purple. They are typically large in shape, with thick walls and a sweet taste.
Cherry Peppers
Characteristics: Small and round, similar in size to cherries, with bright colors. These sweet peppers have a sweet flavor and a crisp texture.
Banana Peppers
Characteristics: Long and slender, their color varies from light yellow to red. They are usually sweet in taste, but some varieties have a slight spiciness.
Italian Sweet Peppers
Characteristics: These long peppers are usually red or green, with a very sweet taste and thicker flesh.
Mini Sweet Peppers
Characteristics: Small, colorful, and high in sweetness. These peppers have a crisp texture and come in a variety of colors.
Cubanelle Peppers
Characteristics: These peppers are longer in shape, with colors ranging from light green to red, and have a more complex flavor than Bell peppers.
Step 2: Choose a growing medium for your hydroponic bell peppers
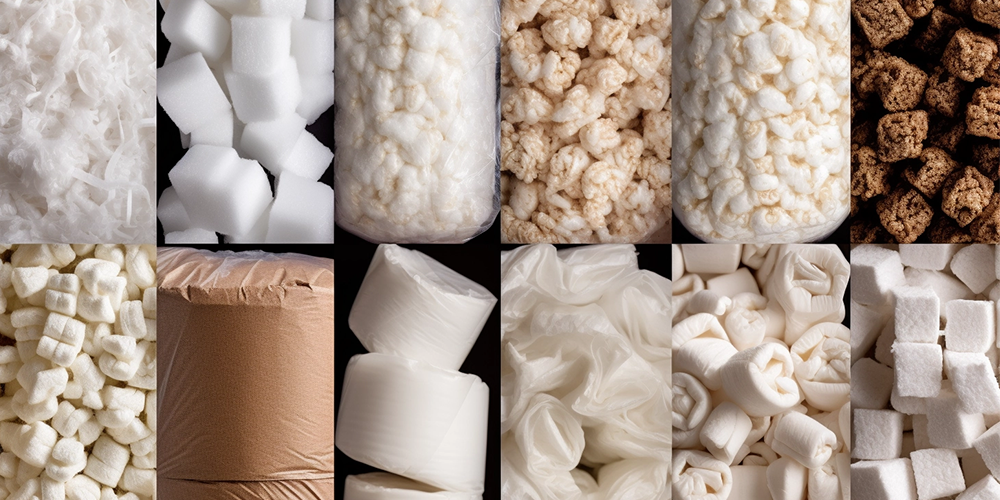

Rockwool
- Characteristics: Highly water absorbent while maintaining good air permeability.
- Best Uses: Ideal for seed germination as it can maintain constant moisture while preventing over-watering.
- Disadvantage: Rockwool fibers can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system during handling, and it is not biodegradable, raising environmental concerns.
Perlite
- Characteristics: Lightweight and porous, providing excellent air circulation.
- Best Uses: Commonly used to improve the drainage and aeration of other mediums, suitable for plants that require good air flow around the roots.
- Disadvantage: Perlite can cause dust, which is harmful if inhaled, and it doesn't hold water as well as other mediums, requiring more frequent watering.
Coco Coir
- Characteristics: Natural and organic, with a good balance of water retention and aeration.
- Best Uses: Suitable for the entire growth cycle, especially for plants that require a consistently moist medium.
- Disadvantage: The quality of coco coir can vary greatly, and it may contain high salt content if not properly rinsed. It also decomposes over time, requiring replacement.
Vermiculite
- Characteristics: Strong water retention capacity, also contains a certain amount of minerals.
- Best Uses: Suitable for plants that need more moisture and nutrients, often mixed with other mediums to increase water retention.
- Disadvantage: Vermiculite has a limited capacity to hold nutrients and can become compacted over time, reducing its effectiveness in aeration.
Clay Pellets
- Characteristics: Hard and porous, providing good support and drainage.
- Best Uses: Suitable for larger or heavier plants, offering stable support while keeping the roots dry.
- Disadvantage: Clay pellets are heavier than other mediums, making them less ideal for systems where weight is a concern. They also require thorough rinsing to remove dust and debris.
Peat Moss
- Characteristics: Highly water-retentive, acidic environment.
- Best Uses: Suitable for seed germination and young plant growth, especially for plants that require a specific acidic environment.
- Disadvantage: Peat moss is acidic, which might not be suitable for all plants. It's also a non-renewable resource, raising environmental sustainability concerns.
Step 3: Prepare your hydroponic bell peppers seeds for germination

Selecting Seeds
- Choose high-quality sweet pepper seeds, preferably varieties suitable for hydroponics. Ensure the seeds are fresh to improve germination rates.
Seed Sterilization (Optional)
- To prevent bacterial infections, seeds can be soaked in a diluted solution of 1/10 bleach or 3% hydrogen peroxide for about 5 minutes, then rinsed thoroughly with clean water.
Preparing the Germination Medium
- Use a medium suitable for germination, such as rockwool cubes, coco coir, or specially designed seed germination pads. Ensure the medium is moist but not overly saturated.
Sowing
- Gently place the seeds on the germination medium. If using rockwool cubes, you can place the seeds into pre-made small holes.
Maintaining an Appropriate Environment
- Place the seeded medium in a warm, moist environment. The ideal temperature range is between 20°C and 25°C. A heating pad can be used to maintain a stable temperature.
Covering and Moisturizing
- Lightly cover the seeds (if necessary) and keep the medium moist. Use a sprayer to regularly spray water to maintain humidity.
Lighting
- Once the seeds begin to germinate, move them to a well-lit area. At this stage, a gentle artificial light source, such as an LED grow light, can be used.
Monitoring and Transferring
- Monitor the progress of seed germination. Once the seedlings have developed true leaves (the first pair of leaves other than the cotyledons), they can be transferred to the hydroponic system.
Step 4: Provide a nutrient solution for your hydroponic bell peppers
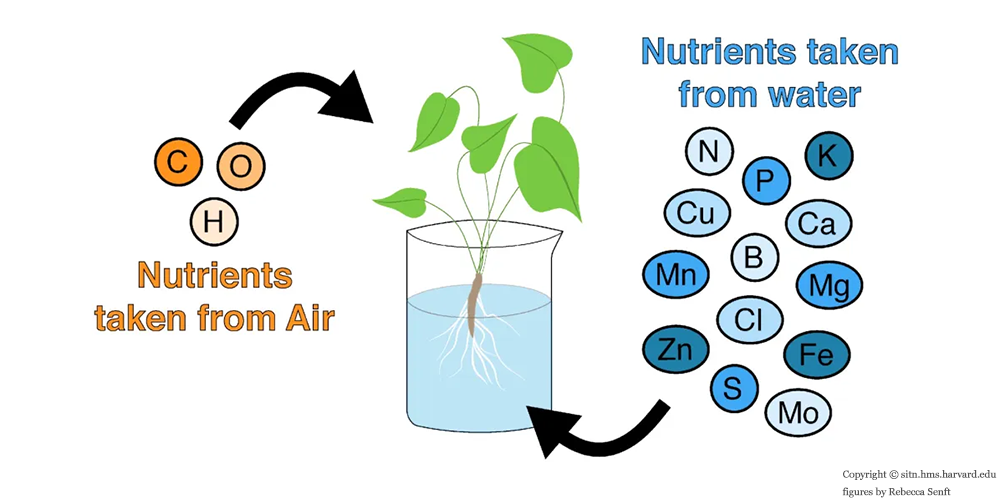
Selecting the Appropriate Nutrient Solution Formula
Hydroponic sweet peppers need a comprehensive and balanced supply of nutrients, including Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Potassium (NPK), as well as micronutrients like calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. There are nutrient solutions available on the market specifically designed for hydroponic vegetables that are suitable for the growth requirements of sweet peppers.
Adjusting the pH of the Nutrient Solution
Sweet peppers grow best in an environment with a pH value between 5.5 and 6.5. Use a pH meter to regularly test the pH of the nutrient solution and adjust it with pH up or down solutions as needed.
Monitoring the Electrical Conductivity (EC) of the Nutrient Solution
The EC value indicates the concentration of dissolved solids in the nutrient solution, i.e., the nutrient strength. The suitable EC range for sweet peppers is typically between 2.0 to 3.5 mS/cm. Regularly check and adjust the EC value to ensure that plants are receiving the right amount of nutrients.
Regularly Changing the Nutrient Solution
To maintain the freshness and effectiveness of the nutrient solution, it is recommended to change it every two weeks. This helps to prevent nutrient buildup and potential disease issues.
Maintaining an Appropriate Water Temperature
The ideal water temperature for hydroponic sweet peppers should be maintained between 18°C to 22°C. Water temperatures that are too high or too low can affect the plant's nutrient absorption and growth.
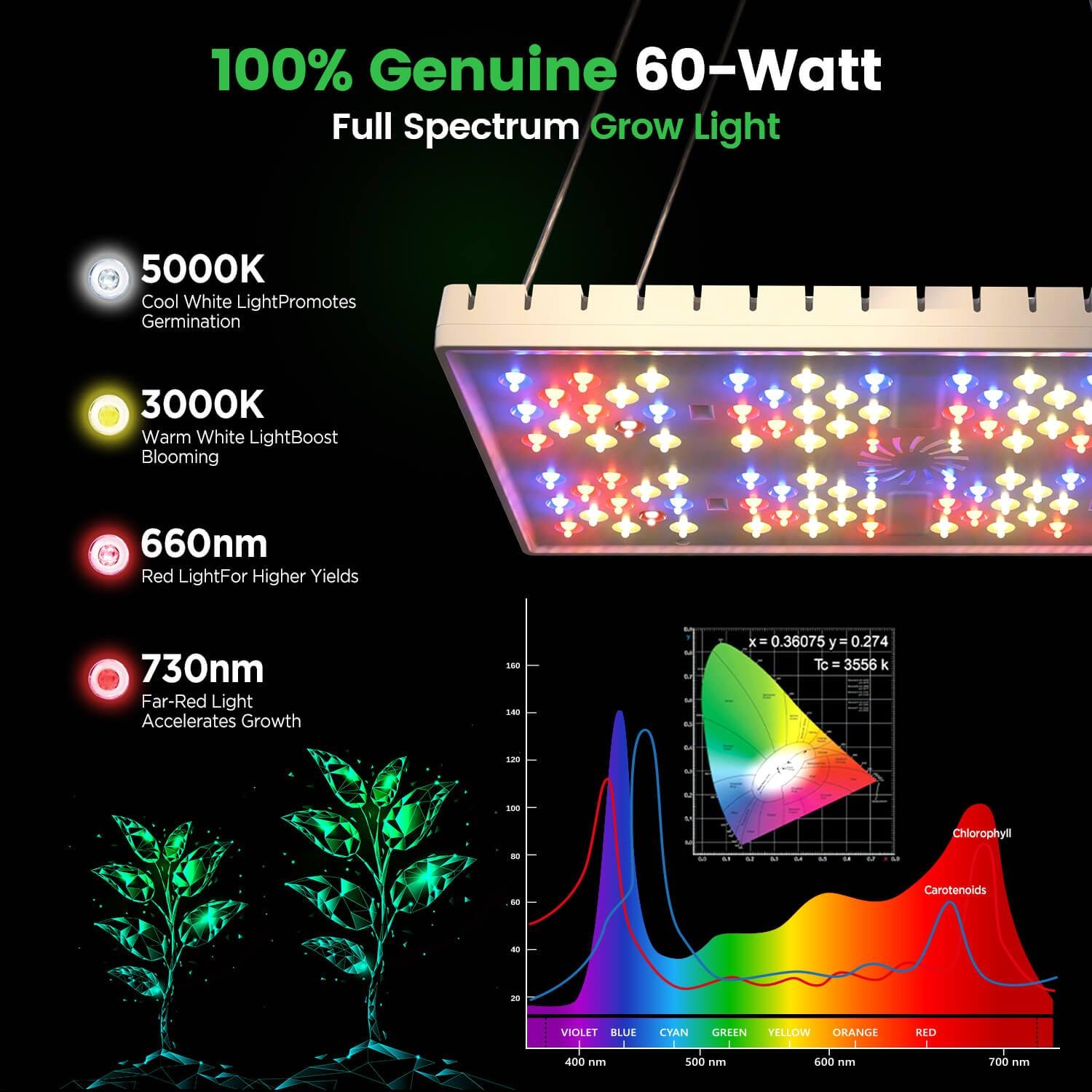
Step 5: Provide artificial lighting for your indoor hydroponic bell peppers
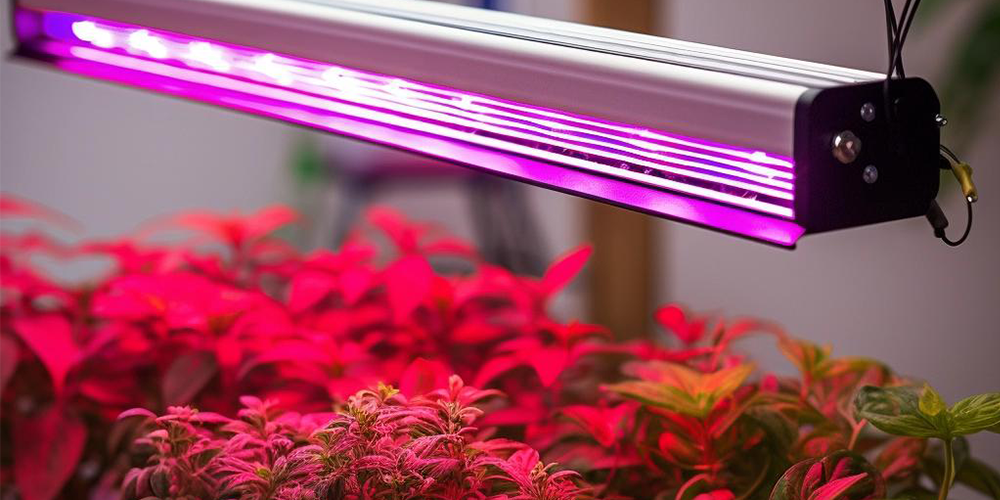

Sweet peppers, as plants with high light requirements, need sufficient lighting when grown in an indoor hydroponic environment. Artificial lighting not only supplements natural light but also allows control over light intensity and duration to optimize the growth and fruit yield of sweet peppers.
Choosing the Appropriate Light Source
- LED Grow Lights: Efficient and energy-saving, they can provide full-spectrum lighting, suitable for promoting the growth and fruit maturation of sweet peppers.
- High-Pressure Sodium (HPS) and Metal Halide (MH) Lights: These traditional light sources are also suitable for plant growth but are generally more energy-consuming compared to LEDs.
Ensuring Adequate Lighting Time
- Sweet peppers typically require about 14 to 16 hours of light per day. Timers can be used to control lighting time, ensuring plants receive a balanced day-night cycle.
Adjusting Light Intensity
- Light intensity is crucial for the growth and fruit development of sweet peppers. Ensure the light fixture is placed at an appropriate distance from the plants, generally recommended to be about 30 to 60 centimeters above the top of the plants, to avoid burning the leaves.
Step 6: Timing and Harvesting of Hydroponic Bell Peppers
Determining the Harvest Time
- The maturity time for sweet peppers depends on the variety, typically starting from 60 to 90 days after planting.
- Mature sweet peppers are brightly colored, fully developed in size, with smooth and taut skin.
- If you are growing a color-changing variety (such as from green to red), waiting for them to completely change color is a good indicator for harvest.
Harvesting Method
- Use sharp scissors or garden shears for harvesting, carefully cutting the stem that connects the plant to the fruit.
- Avoid pulling the fruit directly, as this may damage the plant or the fruit.
Sustainable Harvesting Practices
- Continuous Harvesting: Do not harvest all the fruits at once. Gradually harvest as needed, which can extend the production period of the plant.
- Plant Reuse: After harvesting, check the health of the plant. Healthy plants can continue to be cultivated to produce more fruits.
FAQs - Frequently Asked Questions about Growing Hydroponic Bell Peppers

Q1: Why are my sweet pepper plants developing yellow leaves?
A1: Yellowing of leaves can be due to various reasons, including overwatering, nutrient deficiency, or diseases. Check if the water circulation in the hydroponic system is functioning properly, and ensure the nutrient solution concentration and pH value are appropriate. Also, look for signs of pests or diseases.
Q2: My sweet peppers are growing slowly, what should I do?
A2: Slow growth can be caused by insufficient light, inappropriate temperatures, or nutrient imbalances. Ensure the plants receive enough light, maintain suitable growing temperatures, and regularly check the composition of the nutrient solution.
Q3: Do hydroponic sweet peppers need to be pollinated?
A3: Sweet peppers are self-pollinating plants and typically do not require manual pollination. However, in indoor environments, gently shaking the plants or using a small brush to touch the flowers can help increase pollination rates.
Q4: How can I prevent root rot in hydroponic sweet peppers?
A4: Root rot is usually caused by overwatering or poor air circulation. Ensure your hydroponic system has a good air pump and proper water circulation. Regularly check the health of the roots and keep the nutrient solution clean.
Q5: Why are the fruits on my sweet pepper plants splitting?
A5: Fruit splitting is often caused by uneven water supply. Maintain a stable level of nutrient solution and avoid drastic fluctuations in moisture. Also, keeping indoor temperatures stable can help prevent fruit splitting.
Q6: I have pests on my sweet pepper plants, what should I do?
A6: First, identify the type of pest, and then choose an appropriate biological or chemical control method. In indoor environments, using biological control methods, such as introducing natural predators, is often a safe and effective choice.
Other Plant Hydroponic Growing Tips
If you are also interested in other hydroponic plants, please read related articles.
- The Best 11 Easy-To-Grow Vegetables in Hydroponics
- Top 10 Fruits to Grow in Hydroponic Systems
- Hydroponic Herbs: A Beginner's Top 10 List
- How to grow hydroponic cherry tomatoes Indoors: A Detailed Guide
- How to grow cilantro hydroponically indoors: A Beginner’s Guide
- How to grow Hydroponic Bell Peppers indoors: A Detailed Guide
- How to Grow Hydroponic Blueberries Indoors: A Detailed Guide



















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.