Petunias, beloved as bedding plants, hail from South America and are highly regarded for their profusion of vibrant blooms. These versatile plants have become a staple in many homes and gardens around the world. They are one of many flowers that can be grown in hydroponic growing systems.
In this guide we will look at which types you might grow, cover the basic care requirements, and guide you step by step through the process of growing Petunias in a hydroponic growing system.
Types of Petunia to Grow

Petunias showcase a broad spectrum of floral hues, encompassing tones of pink, purple, red, white, blue, and dual-colour blends. Their distinctive trumpet-shaped blooms typically consist of five fused petals with a central throat, contributing to their visual appeal. Certain cultivars also boast ruffled or double flowers, which further adds to their aesthetic appeal.
Beyond their diverse colour palette, petunias also exhibit a variety of sizes and growth habits. Compact or bushy varieties are excellently suited for lining borders or growing in pots. Meanwhile, trailing or cascading types are perfectly suited for hanging baskets or other raised containers.
When opting for petunias for hydroponic growth, it's crucial to select varieties that adapt well to container gardening and flourish under controlled conditions. Here are some sought-after types of petunias ideal for hydroponic systems:
- Grandiflora Petunias:Recognized for their striking, sizeable blooms, grandiflora petunias boast an extensive spectrum of colours and patterns. They are excellent for injecting a burst of colour into your hydroponic garden.
- Multiflora Petunias:These petunias yield smaller blossoms compared to grandifloras but showcase a profusion of blooms. With their compact nature, they suit container gardening admirably, making them a prime choice for hydroponic systems with limited space.
- Wave Petunias:Characterised by their trailing growth, wave petunias sprawl and drape over container edges, creating an enchanting cascade effect. Low-maintenance and perfect for hanging baskets or vertical hydroponic arrangements.
- Supertunia Petunias:Supertunias exhibit vigorous growth and thrive in high temperatures, producing an abundance of blooms throughout the growing season. Their wide array of colours makes them an excellent fit for hydroponic systems basking in full sunlight.
- Surfinia Petunias: Surfinias, trailing petunia varieties, yield copious flowers and are well-suited for hanging baskets or tall hydroponic towers. Their heat and drought tolerance render them suitable for hydroponic setups in warmer climates.
- Cascadia Petunias: Compact and mound-forming, Cascadia petunias produce an abundance of flowers, making them perfect for container gardening. They are an ideal choice for hydroponic systems with limited space.
- Million Bells Petunias: Also known as calibrachoa, Million Bells offer small, bell-shaped flowers in various hues. They add texture and diversity to hydroponic gardens, complementing other petunia varieties.
The Growth Cycle of Petunias
Many petunias are grown as annuals in temperate climates, while others are perennial and persist in warmer locations to flower over multiple years. Hydroponic indoors growing offers the opportunity to grow petunias year-round, even in locations where they cannot survive outdoors during the coldest part of the year.
From Seed to Flower
The growth cycle of Petunias begins with seed germination, triggered by favourable conditions such as moisture, warmth, and adequate light. Petunia seeds typically germinate within 7-10 days when sown in the right growing medium.
After germination, petunia seedlings emerge, sporting their first true leaves. During this stage, seedlings require gentle watering and sufficient light to promote healthy growth. Once the seedlings develop several sets of leaves, they are ready for transplanting into individual containers or hydroponic systems.
With the establishment of a robust root system, petunias enter a phase of vegetative growth, characterized by the proliferation of foliage and stems. Adequate nutrients, water, and light are essential during this stage to support vigorous growth and prepare the plants for flowering.
As petunias mature, they begin to form flower buds at the tips of their stems. Bud formation is influenced by factors such as temperature, light intensity, and day length. Providing optimal growing conditions encourages abundant bud production.
The culmination of the growth cycle is the flowering stage, where petunias burst into bloom, showcasing their vibrant colours and delicate fragrance. Depending on the variety, petunias may bloom continuously throughout the growing season
From Cutting to Blooms
Petunias can also be propagated by cuttings (though note that with some trademarked plants, vegetative propagation at home is prohibited). Taking cuttings rather than sowing seeds ensures that the offspring will look like the parent plant.
After planting, cuttings will, as above, go through the vegetative stage before they begin to flower.
General Care for Petunias

Wherever you are growing Petunias and whether your hydroponic system is outdoors or inside, there are certain key care requirements that you must remember in order to place and care for your plants correctly.
Light
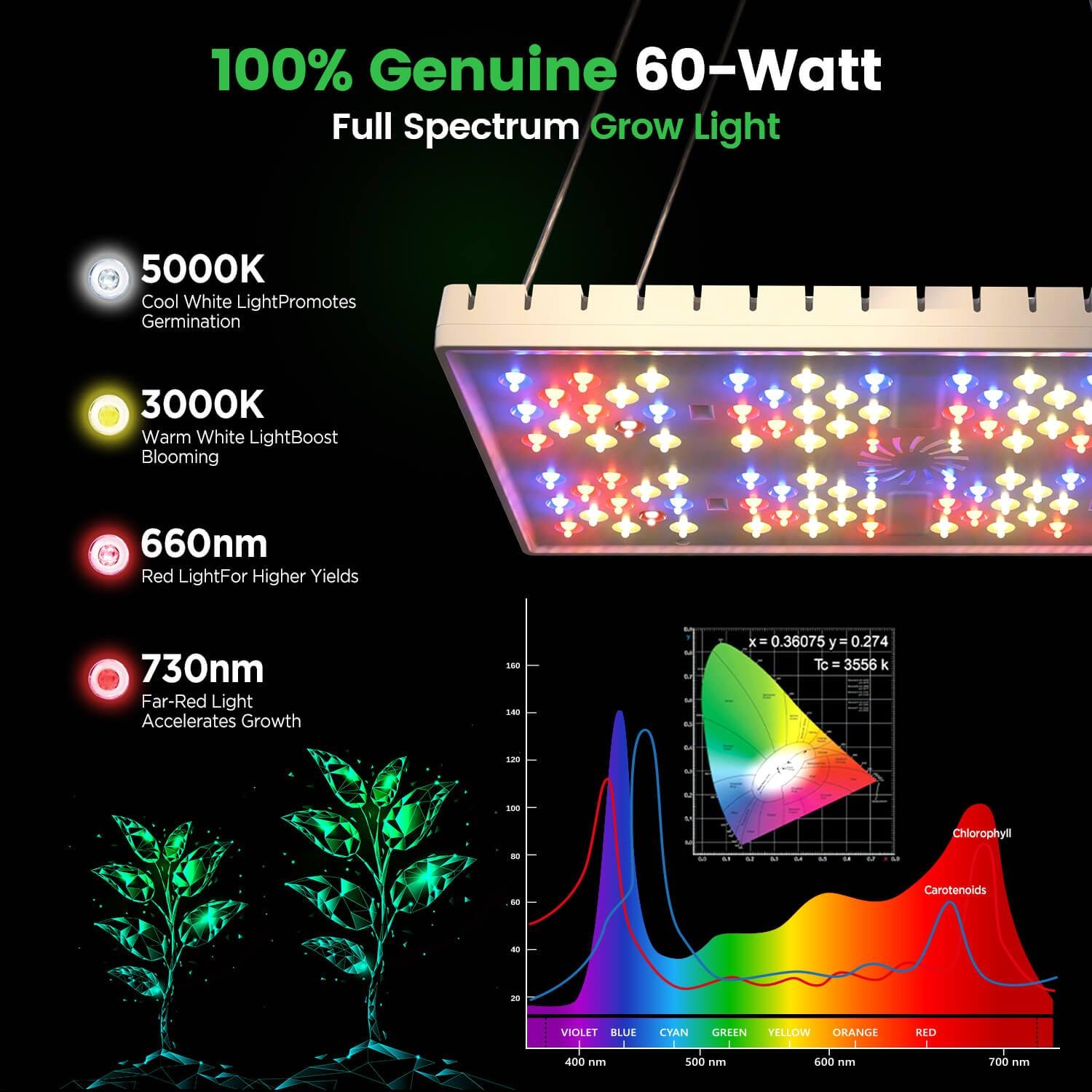
One important thing to remember, for example, is that Petunias thrive in full sunlight, so you need to provide them with at least 6-8 hours of direct sunlight per day if growing outdoors or inside with plenty of natural lighting. If growing indoors, provide supplemental lighting with full-spectrum LED grow lights to make sure they get sufficient light exposure.
Temperatures
Ideal temperatures for Petunias are18-24°C. during the day and 13-18°C at night. Ideally, your hydroponic system should not be too close to a heat source, nor in cold draughts, so that temperatures do not fluctuate too dramatically.
Water and Nutrients
Of course, when you are growing Petunias hydroponically, they will not get nutrients from the soil but rather from the nutrient solution you provide, or the water from a fish tank or fish pond in an aquaponic system.
You need to make sure that the necessary macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (iron, calcium, magnesium) are delivered to your plants.
To make sure nutrients can be taken up correctly, you need to monitor the pH and EC (electrical conductivity) of the nutrient solution regularly, adjusting as needed to maintain optimal levels for petunia growth. Ph should ideally remain between 5.5 and 6.5 and EC between 1.2 and 2.5.
Trimming and Maintenance
No regular trimming is needed with most modern petunias, but sometimes, trimming regularly can help prevent leggy petunia plants.
Regular deadheading can also be beneficial with some varieties and, of course, can help to keep things neat. Deadheading regularly can prolong the flowering period for some types.
Prune Stems and Roots
Though not strictly necessary with all types and varieties, with some Petunias it can be a good idea to pinch out the growing tips to encourage bushier growth.
If you wish for a petunia to remain small enough to remain in a certain pot, then roots may occasionally be pruned too in order to make sure that it does not become pot bound and yet you don't have to move it to a bigger pot.
Growing Petunias Hydroponically – Step By Step

Here is a step by step guide to the process you should follow if you wish to grow these flowers within a hydroponic system:
1. Choose a Petunia Variety
While, as discussed above, there are many different petunias you could choose for your hydroponic system, be sure to choose one suited to the system you have used. For example, choose wave petunias for a vertical tower system, and multiflora or cascadia petunias if space is limited or you are using smaller containers of some kind.
3. Sow Petunia Seeds, Take Cuttings, or Source Young Plants
Be sure to select Petunia seeds from a reputable source – either online or from a local plant nursery. Petunia specialists will have a greater selection for you to choose from.
To cultivate Petunias from seed:
- Start sowing seeds indoors during late winter.
- Scatter seeds evenly on the surface of a seed tray filled with moist, peat-free seed compost.
- Place the seeds in a warm, well-lit location, either covered or in a propagator, to prevent them from drying out. Maintain temperatures around 21 degrees Celsius.
- Once seedlings emerge, transplant them into individual pots, ensuring they are kept in an environment with temperatures ranging from 13 to 25 degrees Celsius.
- Acclimate and transplant your petunia seedlings outdoors (if they are to be grown outdoors) after the threat of frost has passed in your region.
Cuttings are usually taken from Petunias between mid spring and early summer. Cuttings of around 10cm or so should be cut from a mature parent plant with clean, sharp scissors or garden shears. Cut just below a node where leaves meet the stem.
Remove any flowers or flower buds, and lower leaves, so that only a few of the supper leaves remain near the top of the cutting. Dipping the end in rooting hormone is not essential but can help ensure success.
Plant cuttings into a pot well-drained potting mix, so that at least one or two leaf nodes are buried below the surface of the mix. Water but do not overwater, and consider covering to maintain humidity if this is low. Place the pot in a location with bright but indirect light.
One roots form, the petunias can be hardened off and planted out into the garden.
4. Provide a Nutrient Solution

Make sure that your hydroponic system is set up and operational before planting. Ensure that a nutrient solution is available within the system, and ensure that the pH and nutrient levels of that nutrient solution are within the optimal range for petunias.
Carefully remove the petunia seedlings from their containers, taking care not to damage the roots. Gently tease apart any tangled roots and place each seedling into the growing position or growing medium that you have prepared for it.
Position the seedlings in the hydroponic system, ensuring that the roots are fully submerged in the nutrient solution. Space the seedlings evenly to prevent overcrowding and ensure proper airflow and light availability, and make sure that each plant is secured into place, with support structures where necessary.
5. Provide Artificial Lighting
Remember that in addition to the nutrient solution, petunias will also need grow lights when they are not in a position with adequate natural sunlight.
Petunias need a light intensity of 200 to 400 micromoles per square metre per second during the vegetative stage, and 400 to 600 micromoles per square metre per second while in flower.
Lighting should be on for at least 12 hours per day in the vegetative stage and at least 14 hours a day while the plants are in flower.
Make sure the lights provide a balance of red and blue light. Blue light promotes vegetative growth and red light promotes healthy blooms.
Look out for pests and disease. Frequent pests and diseases that might impact hydroponic petunias include aphids, whiteflies, powdery mildew, and root rot. Regularly inspect your plants for indications of infestation or illness, and employ suitable measures to prevent or manage their spread.
6. Trimming and Pruning Stems
Pinch out petunias to encourage bushiness if desired, deadhead regularly, and prune for size and neatness if needed. Otherwise, just keep an eye on your system to keep your petunias happy and healthy over time.
Petunias can thrive in hydroponic systems. However, since it's easy to obtain young plants, using cuttings is recommended for faster blossoming. This method not only accelerates the growth process but also ensures an earlier display of flowers.
FAQs
Can petunias be grown hydroponically?
Yes, petunias can be grown hydroponically with great success. Hydroponic systems provide an efficient and controlled environment for growing petunias, allowing for optimal nutrient uptake and growth.
What hydroponic system is best for growing petunias?
Several hydroponic systems are suitable for growing petunias, including deep water culture (DWC), nutrient film technique (NFT), and drip systems. Beginners may find DWC systems to be the simplest and most effective choice.
What nutrient solution should I use for hydroponic petunias?
Use a balanced hydroponic nutrient solution formulated specifically for flowering plants. Look for a solution that contains essential macronutrients (nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium) and micronutrients (iron, calcium, magnesium) to support healthy petunia growth and blooming.
Do hydroponic petunias require pollination?
While petunias are primarily self-pollinating, you can assist the process by gently shaking the plants or using a small paintbrush to transfer pollen between flowers. This will help ensure the production of seeds and continued flowering.
Can I transplant petunias into soil planters?
Yes, you can transplant petunias from a hydroponic system into soil planters to grow on in a more traditional garden environment. But make sure that you alter conditions gradually so that the plants have time to acclimatise to their new situation.




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.