Cucumbers, as a vegetable widely consumed around the globe, are not only loved for their fresh taste but also highly regarded for their rich nutritional value. With the acceleration of urbanization and the reduction of arable land, people have started looking for more efficient and sustainable cultivation methods to meet the demand for this versatile vegetable. This is the background for the emergence of hydroponic cultivation technology. Hydroponics, as an innovative agricultural technology, not only solves the problem of land scarcity but also makes indoor cultivation possible. By precisely controlling nutrients and environmental conditions, hydroponic systems can efficiently grow healthy cucumbers almost anywhere. In this guide, we will focus on how to utilize hydroponic systems to grow cucumbers at home, allowing you to enjoy the pleasure of freshly harvested cucumbers even in a corner of the city.
Quick Guide: 6 Steps to Easily Grow Hydroponic Cucumbers Indoors
1. Choose the right container and location: Use a transparent container to observe the water level and root health, ensuring it is placed in a location with ample sunlight.
2. Prepare the hydroponic system: Install a Deep Water Culture (DWC) system, including a water pump and air stone, to maintain sufficient oxygen in the water.
3. Select cucumber seeds: Pick high-quality hydroponic-specific cucumber seeds, as the quality of the seeds directly affects plant growth and yield.
4. Nutrient solution and water quality management: Prepare a nutrient solution suitable for cucumber growth, and regularly check the pH value and nutrient concentration of the water, keeping it within the ideal range.
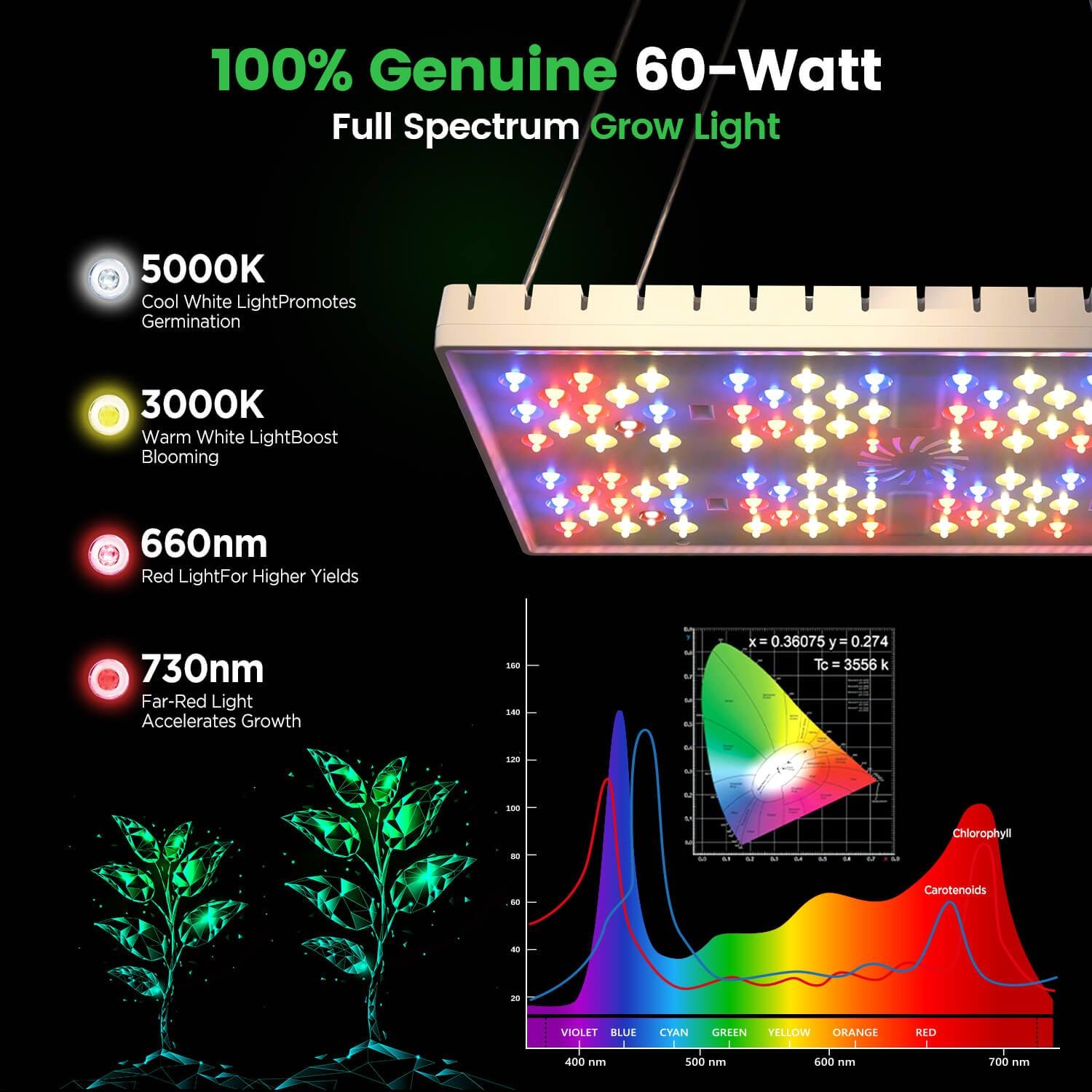
5. Manage lighting: Use LED grow lights to ensure the cucumbers receive enough daily light, simulating the natural light cycle.
Monitoring and maintenance: Regularly check plant health, remove any diseased or weak parts, ensure air circulation, and prevent disease occurrence.
What are hydroponics growing systems?
Hydroponic cultivation, as an efficient soilless farming method, offers various systems on the market, each with its unique characteristics and advantages:
-
Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Structure: In the NFT system, plants are placed in a sloped tube where nutrient solution flows from one end to the other, continuously recycling.
Advantages: Saves water and nutrients since the system recirculates them. Suitable for leafy vegetables like lettuce and spinach.
Disadvantages: Roots may dry out due to exposure to air; high dependency on electricity to continuously pump the nutrient solution.
-
Ebb and Flow
Structure: Controls the inflow and outflow of the nutrient solution with a timed pump, simulating natural tidal movements.
Advantages: Suitable for a variety of plants; irrigation cycles can be adjusted according to the growth stage of the plant.
Disadvantages: The system is complex, requiring timed control of the irrigation cycle, with a high dependency on electricity and timers.
-
Wick System
Structure: One of the simplest forms of hydroponics, using a rope or towel as a "wick" to transport the nutrient solution from the container to the plant roots through capillary action.
Advantages: Does not require electricity, has simple operation, low cost.
Disadvantages: Not suitable for plants with high water needs; lower efficiency in nutrient transportation.
-
Deep Water Culture (DWC)
Structure: In a DWC system, plants are suspended above a container filled with nutrient solution, with roots directly immersed in the water. The container usually also has an air pump and air stone to increase the oxygen content in the water.
Advantages: Roots have direct contact with the nutrient solution, promoting rapid growth. The system is relatively simple and easy to maintain, very suitable for both beginners and professionals.
Disadvantages: A continuous power supply is needed to keep the air pump working to prevent root oxygen deficiency. Larger plants may require additional support.
The DWC system is favored by many hydroponic enthusiasts for its simplicity, efficiency, and wide applicability. It is particularly suitable for indoor environments, allowing effective control over nutrients and environmental conditions, thereby improving crop growth speed and yield. Although each system has its specific application scenarios and limitations, the DWC system, with its excellent performance and ease of use, has become the preferred choice for many indoor hydroponic cultivators.
How do you set up an indoor hydroponic growing system?

To DIY an indoor Deep Water Culture (DWC) hydroponic system, you need to prepare the following basic components and materials. This system is simple to set up and very suitable for beginners.
DIY Deep Water Culture (DWC) Hydroponic System Equipment List:
- Container: Choose a sufficiently deep container, such as a plastic storage bin or a specialized hydroponic container, to hold the nutrient solution.
- Net pots: These baskets will be placed at the top of the container to hold the plants and the plant growth medium.
- Plant growth medium: Peat moss sponges, are used to support the plants and maintain moisture at the roots.
- Air and water pumps: The air pump is used to supply oxygen to the nutrient solution, while the water pump helps to disperse bubbles, ensuring the roots receive ample oxygen.
- Nutrient solution: Choose a hydroponic nutrient solution suitable for the growth of plants like cucumbers.
- pH testing kit: Used to test and adjust the pH of the nutrient solution to ensure it is within the ideal range for plant growth.
- Water level indicator (optional): Helps monitor the water level in the container.
- LED grow lights: If indoor lighting is insufficient, LED grow lights can provide the necessary light.
Setup Steps:
- Prepare the container: Cut appropriately sized holes in the lid of the container for placing the net pots.
- Add nutrient solution and water: Mix the nutrient solution with water according to the instructions, and pour into the container until the appropriate water level is reached.
- Adjust pH: Use the pH testing kit to test the pH of the nutrient solution and make necessary adjustments.
- Place the plants: Insert the plants along with their growth medium into the net pots, ensuring the roots can reach the nutrient solution.
- Set up lighting: Adjust the position and lighting time of the LED grow lights according to the needs of the plants.
By following these steps, you can successfully set up a simple indoor DWC hydroponic system and start growing cucumbers. Remember to regularly check the water level and the condition of the nutrient solution to ensure healthy plant growth.
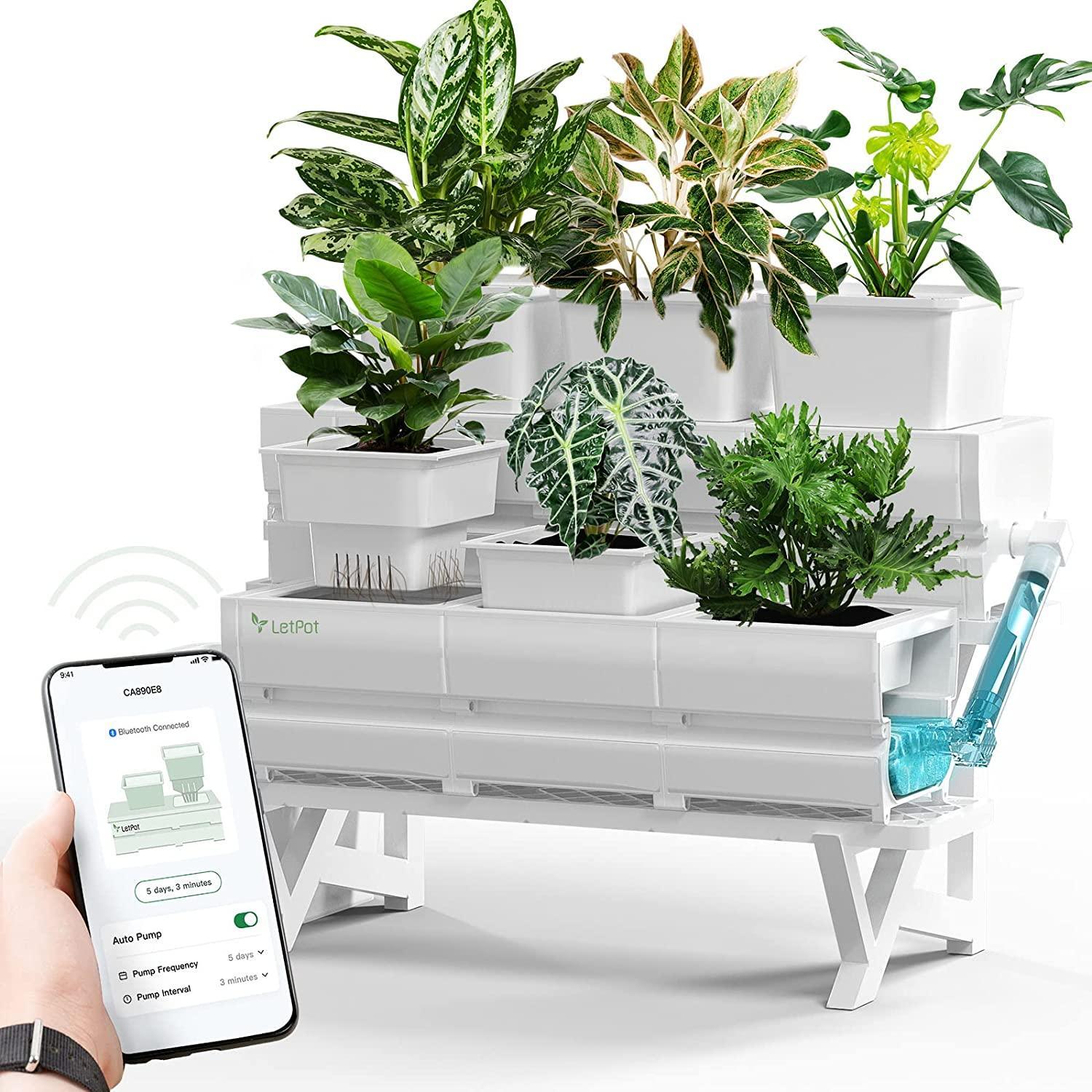
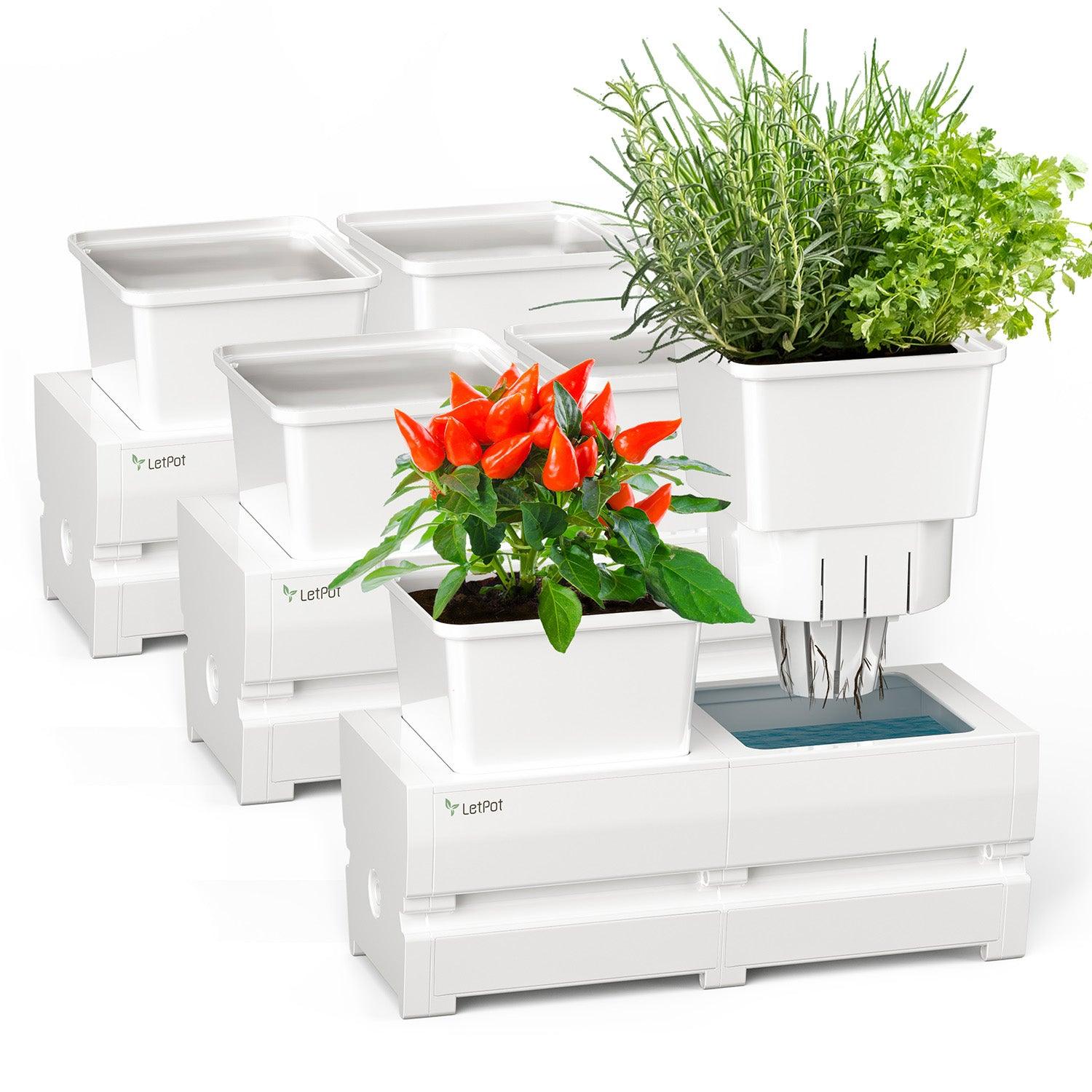
However, I understand that preparing all of this can be challenging for beginners, and you also need to acquire specialized knowledge. Fortunately, many new intelligent hydroponic growing systems are available, making starting your indoor hydroponic garden easier.

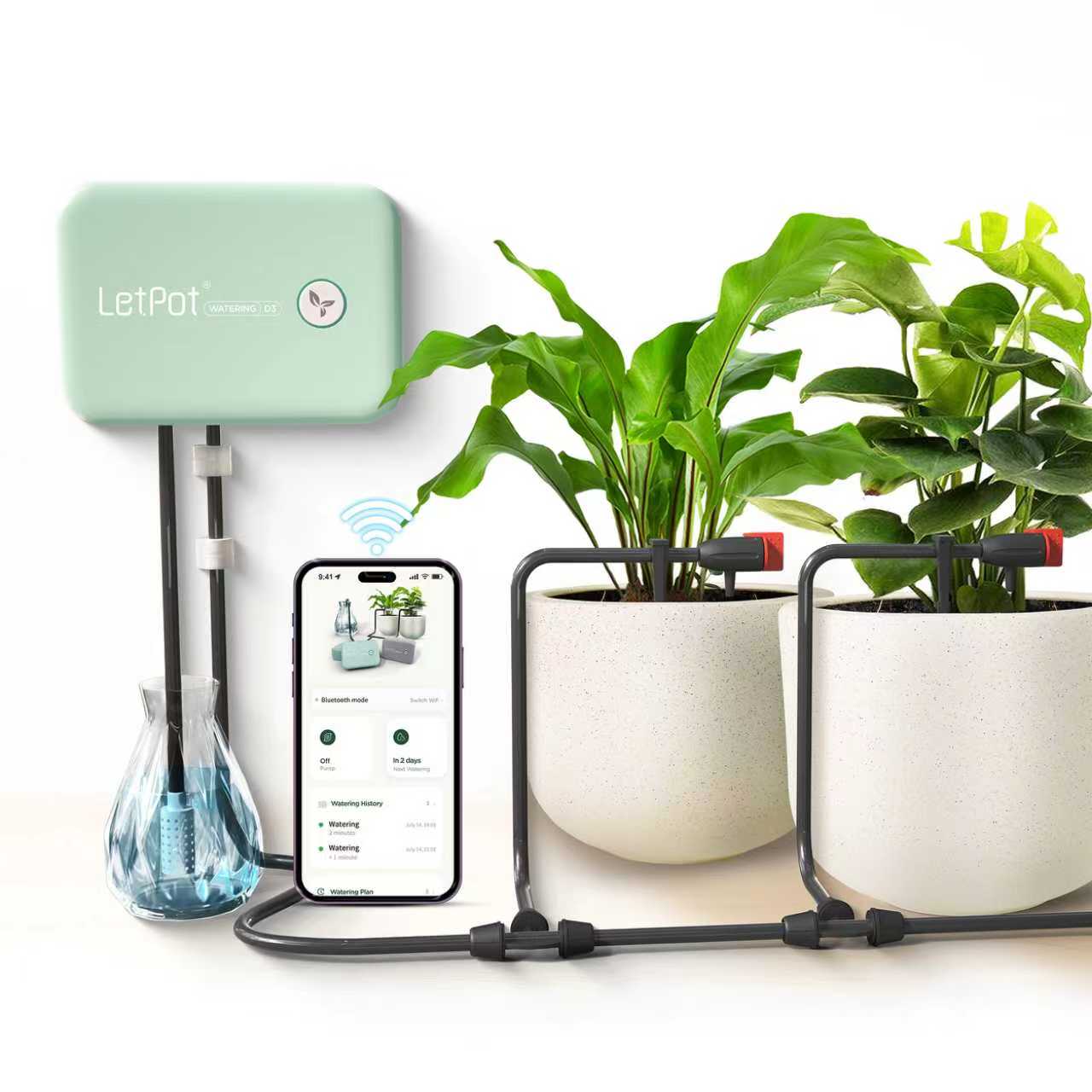
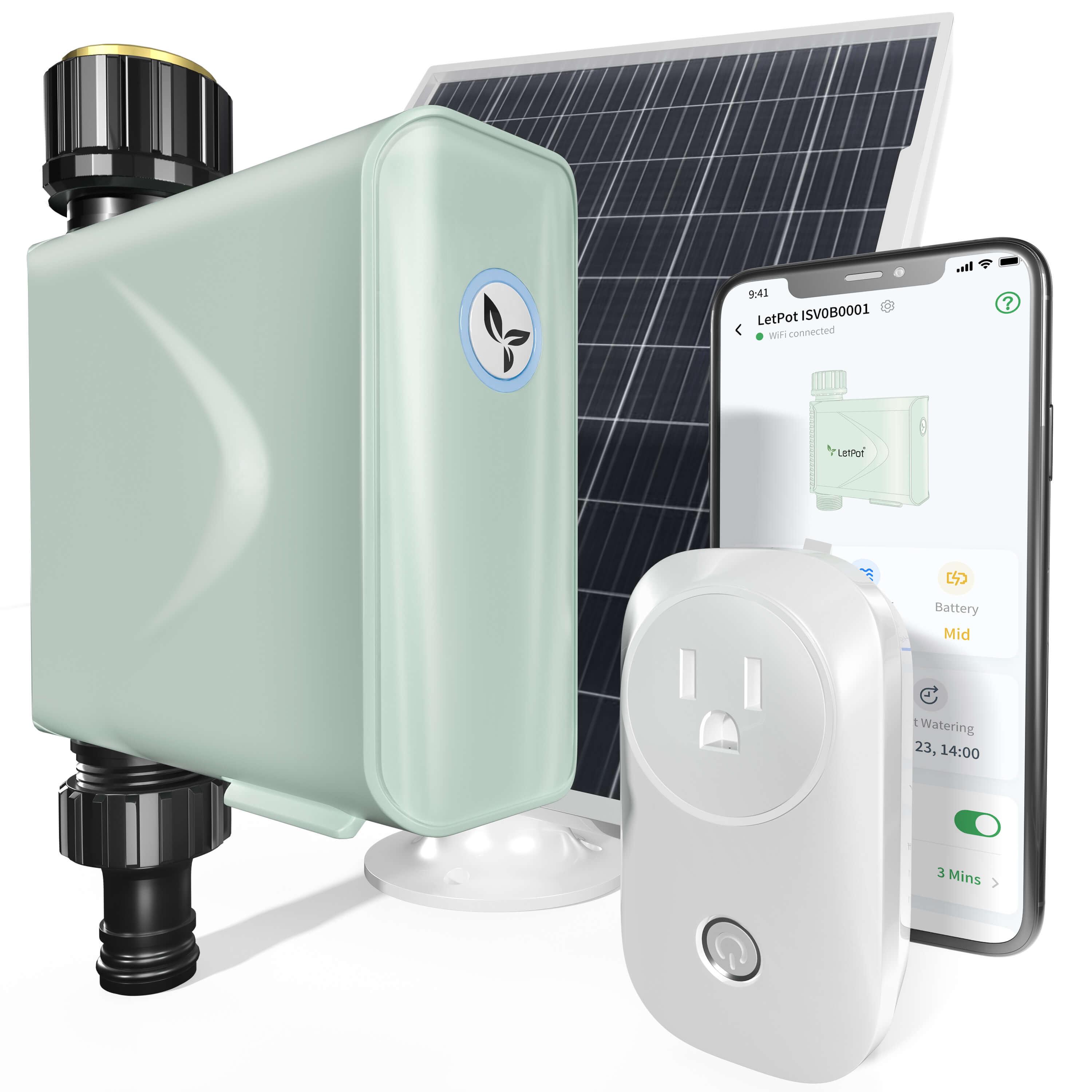
If you're interested, try the LetPot Hydroponics Growing System, which features innovative automatic watering and nutrient functions and integration with an app. With these features, you can effortlessly begin hydroponic cultivation, even if you're a novice gardener.
Learn about LetPot® and customer stories:
- Growing Cherry Tomatoes Indoors: A Personal Tale of Juicy Rewards
- Enjoy Growing Cherry Tomatoes At Home - LetPot Indoor Hydroponic System
How to grow hydroponic cucumbers indoors? (Step-by-step guide)
Step 1: Choose a hydroponic cucumber variety
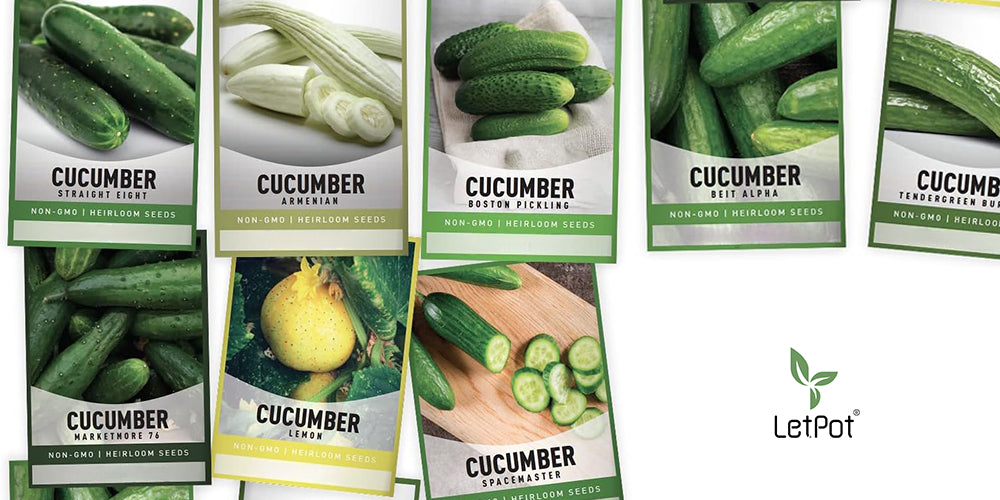

Cucumbers are a versatile vegetable widely used in various cooking and dietary habits, from raw consumption to pickling, and are very popular. Choosing the right cucumber variety can greatly enhance your culinary experience, while also meeting specific nutritional needs. Here are some popular cucumber varieties along with their advantages and culinary uses:
-
English Cucumbers
- Advantages: Thin skin, few seeds, crisp and tender texture, almost no need to peel or deseed.
- Culinary Uses: Very suitable for raw consumption, such as in salads, sandwiches, or as part of cold dishes.
-
American Cucumbers
- Advantages: Thicker skin, high water content, crisp texture.
- Culinary Uses: Suitable for various purposes, including raw consumption and pickling.
-
Japanese Cucumbers
- Advantages: Long and slim, thin skin, almost seedless, crisp and tender texture.
- Culinary Uses: Suitable for raw consumption, making sushi, or Japanese side dishes.
-
Persian Cucumbers
- Advantages: Small, thin skin, few seeds, sweet and crispy texture, very juicy.
- Culinary Uses: Very suitable for raw consumption, such as in salads, or lightly pickled.
-
Gherkins or Cornichons
- Advantages: Very small and crisp, with a unique flavor.
- Culinary Uses: Usually used for pickling, as an appetizer, or side dish.
Benefits
- Nutrient-rich: Cucumbers contain a variety of vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin K, vitamin C, and potassium, which are beneficial for health.
- Low in calories: High water content and low calories make cucumbers an ideal choice for weight loss and healthy eating.
- Versatility: Cucumbers can adapt to various cooking methods, from raw consumption to pickling, providing unique flavors and textures.
- Hydration: High water content helps maintain hydration balance, especially in hot weather.
Step 2: Choose a growing medium for your hydroponic cucumber

Step 3: Prepare your hydroponic cucumber seeds for germination




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.