If you garden indoors, you will of course be responsible for meeting the water needs of all your plants. Seeking out indoor garden water saving ideas can help you to grow more sustainably while keeping plants happy and healthy.
Understanding Water Use in an Indoor Garden
First things first, it can be helpful to make sure you understand how plants use water, and what determines how much water they will use.
What is Transpiration and How Does it Work?

Transpiration involves the movement of water through a plant and its subsequent evaporation from above-ground parts like leaves, stems, and flowers. This process occurs passively, meaning the plant does not use any energy to facilitate it.
The movement of water through a plant, driven by transpiration, serves several crucial functions:
- It transports soluble minerals to areas where they are needed for growth.
Plants require a variety of nutrients in different quantities based on their species and growth stages. Essential nutrients from the soil include nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, while carbon, oxygen, and hydrogen are obtained from the air.
Other important soil nutrients are magnesium, calcium, and sulphur. Gardeners can enhance plant growth and improve flowering and fruiting by adding fertilizers, whether synthetic or natural.
- It supplies water, an essential component for photosynthesis, to the leaves.
- It maintains cell turgidity, providing structural support and helping plants remain upright.
- It aids in cooling the plant, as the evaporation of water from leaf surfaces removes excess heat.
What Impacts How Much Water Plants Need?
How much water plants need depends in large part on the environmental conditions. The following areas are the key things to look at.
Light Exposure: Plants exposed to full sunlight need more water compared to those in shaded areas due to higher rates of transpiration and evaporation.
Temperatures: Plants in hot conditions need more water due to increased evaporation rates, while plants in cooler environments need less.
Humidity Levels: High humidity reduces water loss from plants, decreasing their water needs, while low humidity increases water loss, necessitating more frequent watering.
Wind/ Breezes: Windy conditions can increase the rate of water loss from plants through transpiration, requiring more frequent watering. Indoors, being placed in a draught may have the same effect.
How much water plants use may also depend on:
- The specific species – some plant species need far more water than others.
- The growth stage of the plants in question.
- The health of the plant.
- The soil or growing medium used.
- The size of pots or containers.
Why Try to Use Less Water When Growing Indoors?

You may wonder why it matters how much water you use in your indoor garden. The answer is that it is always important to conserve fresh water, for the planet, and for ourselves.
The Importance of Conserving Fresh Water
Conserving fresh water is essential regardless of where you live, how much rainfall your area receives, or how readily available water appears to be. Fresh water is one of Earth's most crucial natural resources. Many regions are already experiencing fresh water scarcity, a problem that is becoming increasingly common.
The fresh water crisis is largely driven by human activities such as deforestation, agricultural practices, industrial processes, and the misuse of water resources. These issues are further aggravated by global warming and changes in weather patterns.
Additionally, individuals and households contribute to the problem through careless water use, inefficient appliances, and unnecessary activities like excessive lawn watering and car washing. In developed countries, there is often a lack of awareness about the global water cycle, leading to the misconception that fresh water will always be plentiful.
Adopting sustainable water practices is crucial for ensuring that fresh water remains available to meet our needs. By ending harmful practices and implementing methods for sustainable water storage and usage, we can secure fresh water supplies for future generations.
Why Using Less Tap Water Saves Energy and Helps the Environment
As well as thinking about how much water we use for an indoors garden, we should also think about where the water that we use comes from. Ideally, we should all try to reduce our use of mains supply tap water in our indoor gardens.
Using less tap water means we can save energy that would have gone into cleaning and treating that water. So reducing tap water use helps the environment.
What Water to Use in an Indoor Garden
Rather than using tap water it is a good idea, wherever possible, to use rainwater that you have harvested on your property. Using rainwater is the best policy when we can because rainwater is better for your plants as well as the more environmentally friendly option.
Rainwater is free of chemicals such as chlorine and sodium, which can accumulate in the soil from regular irrigation and hinder healthy plant growth when present in high concentrations. Rainwater also contains nitrates and has higher oxygen levels compared to tap water.
Some Key Water Saving Ideas for Your Indoor Garden
Even when we are using rainwater rather than water from a faucet or tap, we should aim to save water. So, here are some key water saving ideas to consider for your indoor garden:
1. Make Water-Wise Plant Selections

First things first, remember that the choices you make about which specific plants to grow will determine how much water you use. Whatever strategies you employ and growing systems you choose, some plants will always need much more water than others. Selecting low-water-use plants can make it easier to conserve water in your indoor growing setup.
2. Choose Pots and Other Containers Carefully
When growing in soil or a soil-based or soil-like growing medium, the pots or containers that you choose are another factor that will determine how much water you use.
Smaller pots and containers will typically lose water more quickly. Losses through evaporation from the surface of the growing medium mean that in smaller pots and containers, plants will need to be watered more frequently.
The porosity of the containers also matters. Plant pots and other containers made from porous materials will lose water more quickly.
And since black or dark-coloured materials absorb light and heat, the soil or potting mix within them will heat up and, again, lose water more quickly than that within white or lightly coloured containers.
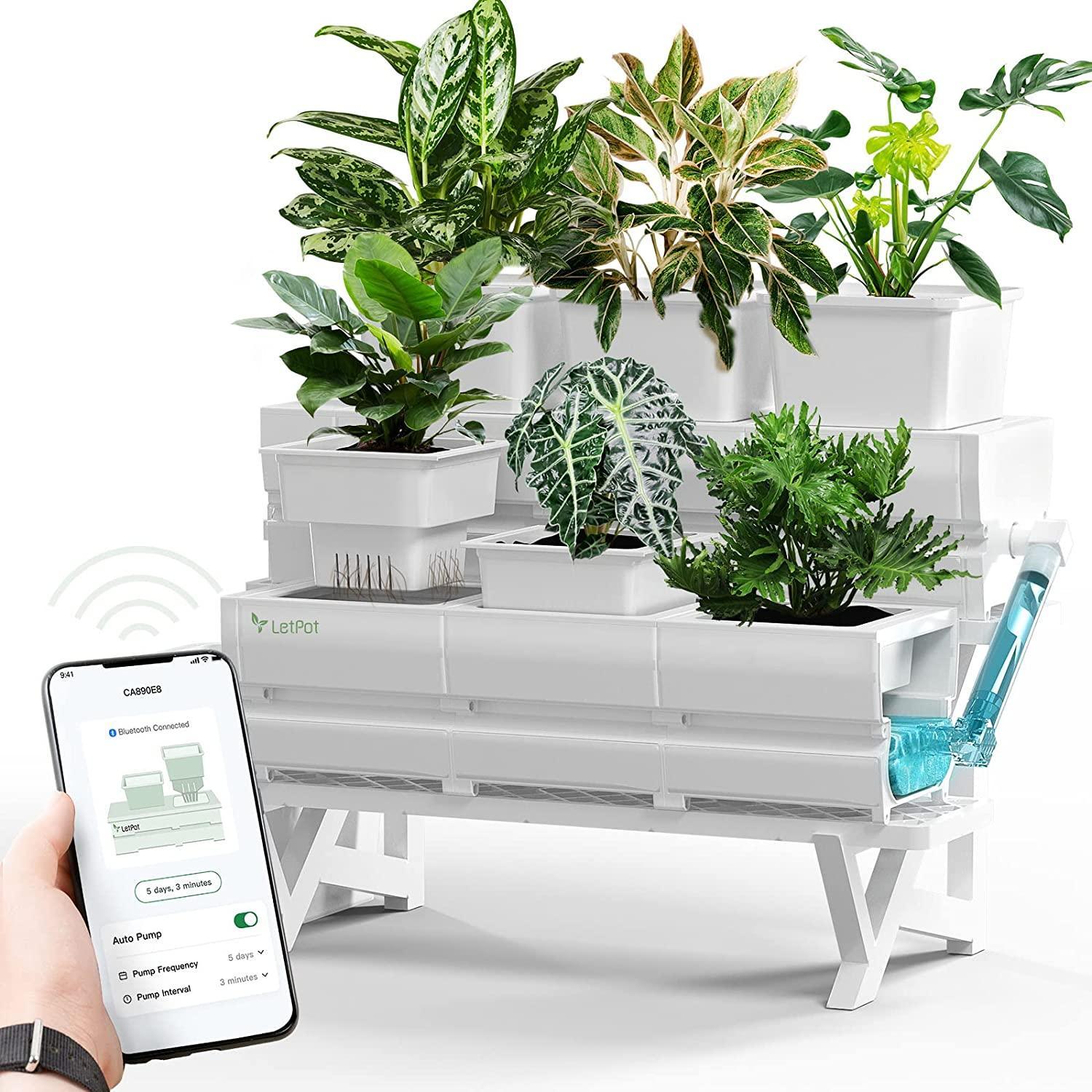
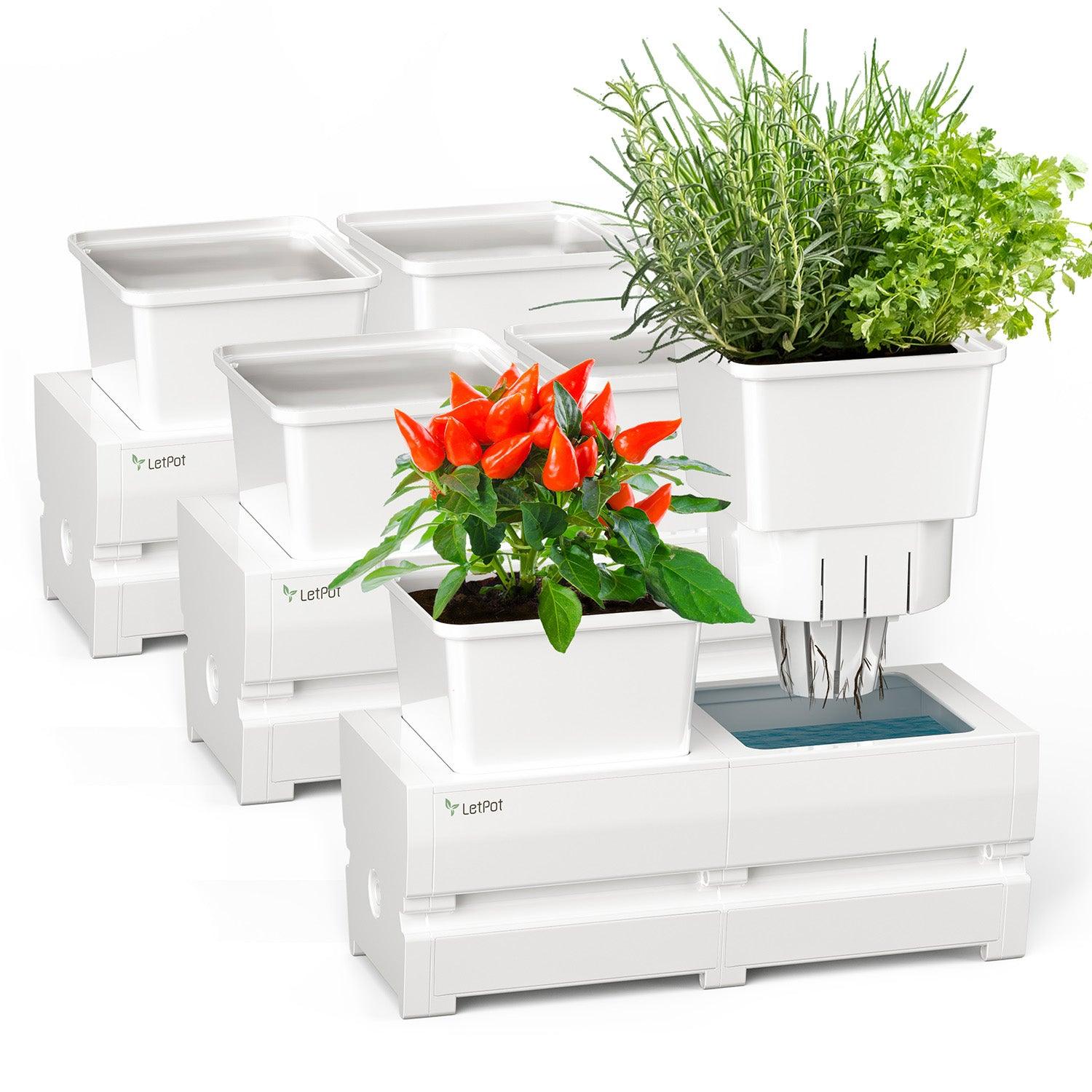
3. Consider Self-Watering Planters

Self-watering planters, with a reservoir of water at the base, are a great water-saving idea. Since water is where it is needed, at the base by plant roots, water is not lost to evaporation as much, or wasted as it is splashed around.
Using these kinds of solutions can mean that you use considerably less water than if you try to water your indoor garden by hand.
4. Water at the Right Times
If you are watering by hand, when you water is just as important as how you do so. It is best where possible to water your plants early in the morning when they are subjected to natural daylight patterns. Watering in the heat of the day is generally not a good idea, and watering late, towards the evening, can exacerbate fungal issues or make such issues more likely to arise.
Of course, the times of watering will be less relevant when you are using grow lights rather than relying on natural daylight. But it can still be a good idea to think about when these lights are turned off and on. Remember that the light (and heat) from grow lights will also have a bearing on how much water you use.
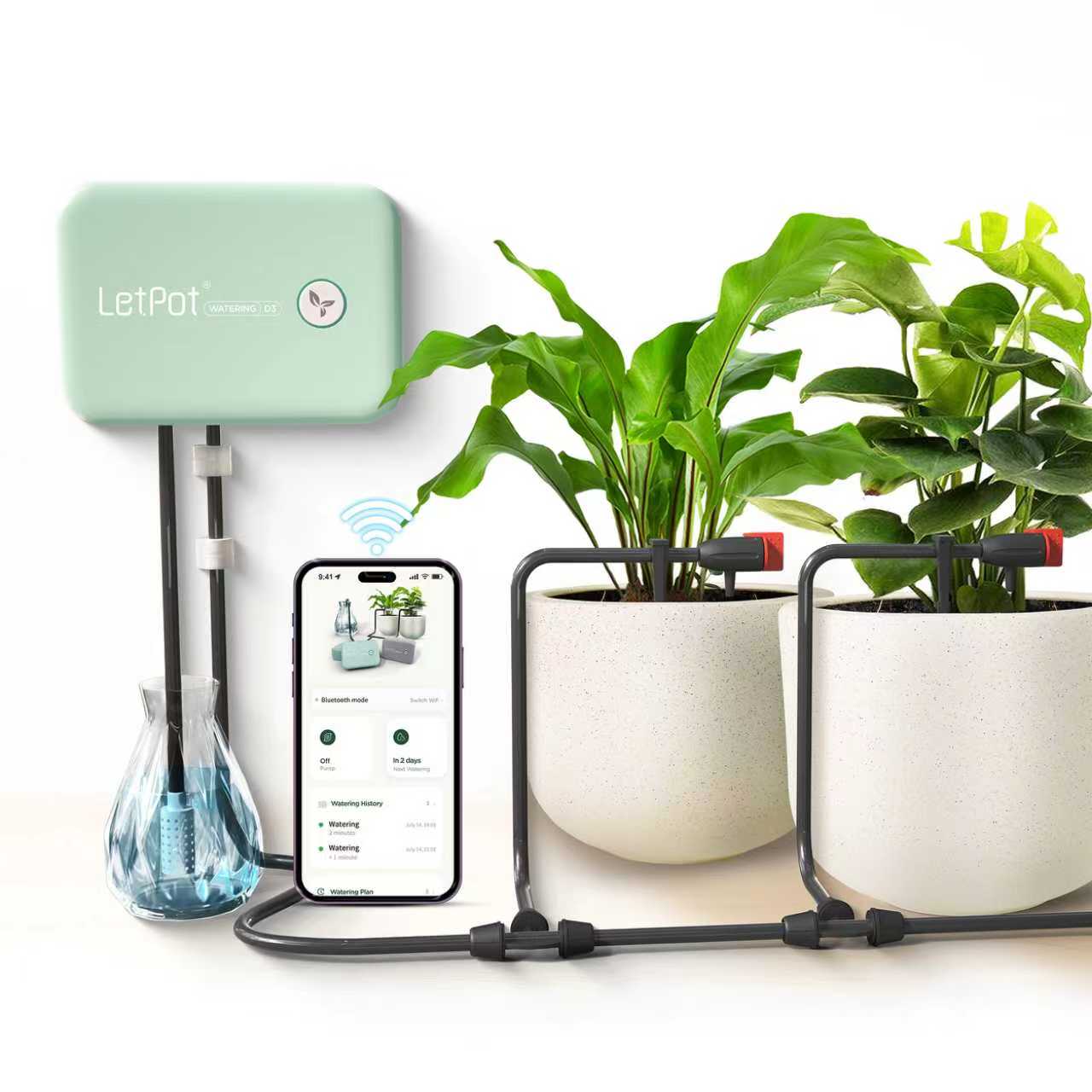
5. Use an Automatic Watering System for Plants

Using an automated watering system can help you to conserve water. You can configure such a system to ensure that you only use exactly the amount of water that is required and no more.
An automated system can help you to avoid issues that arise with under or over watering due to human error, and make sure that your plants in your indoor garden get exactly what they need.
Many gardeners find that when they adopt an automatic watering system, they reduce the amount of water that they use over time.
6. Consider a Hydroponic or Aquaponic System
Adopting a hydroponic or aquaponic system is another way to save water, and switching to such systems can lead to a really significant reduction in water use.
By growing plants in water rather than in soil, and creating a closed-loop, sustainable system, you can grow in a way that uses far less water than traditional growing systems.
7. Implement a Drip Irrigation System
There are numerous options for irrigating crops in an indoor garden or outside. A drip irrigation system is a method that can use far less water than other options because it delivers small amounts of water in a very targeted way – placing that water close to plant roots where it is needed.
Drip irrigation systems make it easier to keep plants' leaves dry, reducing the incidence of fungal infections, as well as saving water. And one that is well designed and installed can be extremely practical and easy to use too.
8. Group Plants With Similar Water Needs Together
When thinking about how to save water, how you decide to layout your garden can also be key. To make sure you do not use more water than you need to, you should make sure that you group plant together that have similar watering needs.
Then you can ensure that watering or irrigation takes those needs into account, and you can deliver less water to areas with drought-tolerant plants, and more to areas with those plants that require more water.
9. Monitor the Moisture in the Growing Medium
Observation skills and monitoring can be crucial to making sure you are not using more water than you need to use. Rather than just watering to a set schedule, you should always tailor your watering or irrigation to suit the reality of the situation.
Remember, there are a wide range of environmental factors and other things that influence how much water plants need and how quickly they and the growing medium they are in will dry out.
So it is always best to check the moisture in the growing medium, either manually or with higher-tech means, before deciding whether more water is required.
10. Keep Things Cooler
Looking at the environmental factors themselves is also crucial to water saving for an indoor garden. Simply by reducing temperatures, for example, we can keep water use down. We might keep temperatures down in a range of ways.
One crucial thing to look at, for example, is switching out hot grow lights for cooler LED grow lights.
11. Look at Humidity, Airflow and Ventilation
Humidity, airflow and ventilation are other things that can influence temperatures and water use in an indoor garden.
Remember, too, that plants will need more water in less humid conditions, and use less in a more humid environment. Good airflow with a lack of overcrowding and good plant spacing, and good ventilation of growing spaces, can help to regulate temperatures and humidity.
12. Use Mulch on the Soil Surface in Pots or Other Containers
Last but not least, if you are growing in a potting mix of some kind, there is one more strategy you can and should use to reduce water losses from the growing medium: mulching.
Laying an organic mulch such as a homemade compost or leaf-mould can help to reduce evaporation from the surface of the soil, and can also reduce the rate of transpiration by keeping the growing medium more cool.
If you do not already mulch around the tops of containers in your indoor garden, then this is one more thing you should consider doing to save water.
Bear these water saving ideas in mind for a more eco-friendly, sustainable indoor garden.du



















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.