1. Definition: Hydroponic Growing System vs. Aeroponics Systems

1.1. Introduction to Hydroponic Growing System and Aeroponics System
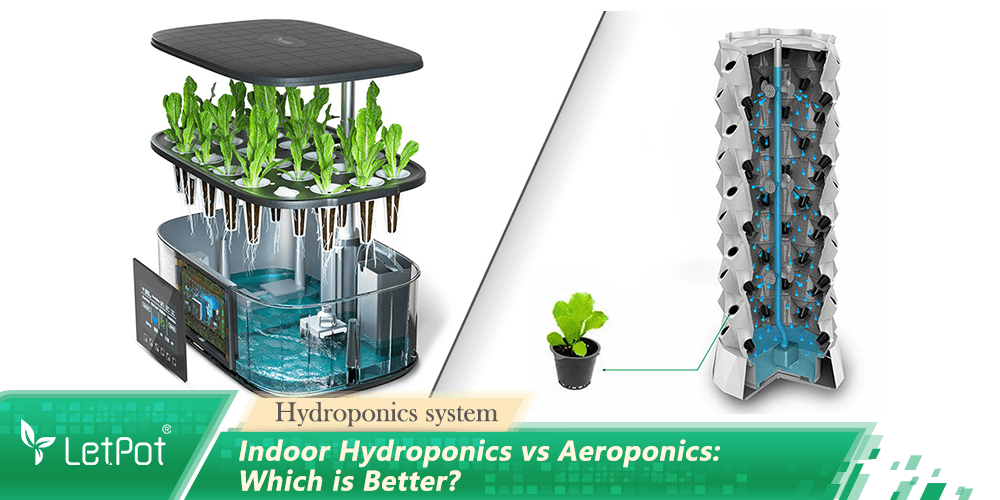
Hydroponics is a method of growing plants in a soil-less environment, relying on a nutrient solution to provide all the necessary nutrients for the plants. In this system, the roots of the plants are directly exposed to water rich in nutrients, allowing them to absorb the nutrients directly. This method eliminates many uncertainties in the soil and allows farmers to control the nutrient intake of plants more precisely.
1.1.1. Principle and Working Method
The core of the hydroponic system is the nutrient solution, a specially formulated liquid that contains all the necessary nutrients for plant growth. The roots of the plants are either fully or partially immersed in this solution, allowing them to absorb nutrients directly from the solution. Since there is no soil as an intermediary, nutrient absorption by the plants is more efficient.
1.1.2. Common Types of Hydroponic Systems
There are various hydroponic systems to choose from, including deep water culture, nutrient film technique, and drip systems. Each system has its unique working method and advantages, suitable for different applications and environments.
1.2. Introduction to Aeroponics Systems
Compared to hydroponics, aeroponics is a more advanced planting technique where the roots of the plants are not immersed in water but are suspended in the air. By using sprayers to spray the nutrient solution onto the roots of the plants, the plants can absorb nutrients from the atomized solution.
1.2.1. Principle and Working Method
In aeroponics systems, the roots of the plants are exposed to a highly oxygenated environment, which promotes healthy growth. Sprayers periodically spray the nutrient solution onto the suspended roots, ensuring the plants receive the nutrients they need.
1.2.2. How Aeroponics Systems Work
Implementing aeroponics requires special equipment, such as sprayers and timers, to ensure that the roots of the plants receive the nutrient solution periodically. Additionally, aeroponics systems typically require more precise environmental control to ensure optimal growth conditions.
2. Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydroponic Growing System and Aeroponics System
2.1. Advantages of the Hydroponic Growing System
Hydroponics, as a mature soil-less planting method, has been widely applied in various agricultural projects. Its main advantages include:
2.1.1. Water-saving:
Compared to traditional soil cultivation, hydroponics can significantly reduce water usage since the water in the system can be recycled.
2.1.2. Efficient Space Utilization:
Hydroponic systems are typically more compact, allowing for more plants to be grown in a limited space.
2.1.3. Faster Growth Rate:
Since plants can directly absorb nutrients from the nutrient solution, their growth rate is typically faster than soil cultivation. Having a lighting system can provide 24-hour illumination, allowing plants to undergo photosynthesis.
2.1.4. Fewer Disease and Pest Issues:
Without soil, many soil-borne diseases and pests cannot thrive in hydroponic systems.
2.1.5. Hydroponic size for portability:
Compact Size, Suitable for Any Indoor Placement
2.2. Disadvantages of the Hydroponic Growing System
However, hydroponics also has its limitations and challenges, mainly including:

2.2.1. Higher Initial Cost:
Setting up a hydroponic system might require a significant initial investment, especially for larger systems.
2.2.2. Dependence on Electricity:
Most hydroponic systems rely on electric pumps and lighting equipment, necessitating a stable power supply.
2.2.3. Technical Expertise Required:
Successfully operating a hydroponic system requires certain knowledge and skills, especially regarding plant nutrition and pH balance.
2.2.4. Hydroponics Size Limitations
Compared to Aeroponics, Fewer Planting Holes and Smaller Plant Size
2.3. Advantages of Aeroponics Systems

Aeroponics, as a relatively newer technique, also has its unique benefits:
2.3.1. Abundant Oxygen Supply to Roots:
Since the roots of the plants are directly exposed to the air, they can receive a large amount of oxygen, promoting healthy growth.
2.3.2. Rapid Growth Rate:
Similar to hydroponics, aeroponics also allows plants to absorb nutrients directly from the atomized solution, with more precise spray heads, it's more water-efficient, and typically has a larger planting capacity with more holes.
2.3.3. Water Conservation:
Even though aeroponics uses sprayers, it remains an efficient method of water usage as the water in the system can also be recycled. Moreover, it's even more water-saving.
2.3.4. Reduced Risk of Diseases:
Like hydroponics, aeroponics systems also reduce the risk of soil-borne diseases.
2.4. Disadvantages of Aeroponics System:
However, aeroponics also faces some challenges:
2.4.1. High Technical Complexity:
Aeroponics systems typically require more precise control and maintenance to ensure the roots of the plants receive appropriate nutrient supply.
2.4.2. Continuous Power Supply Needed:
Like hydroponics, aeroponics also relies on electricity to power sprayers and other equipment. However, most don't have lighting equipment.
2.4.3. Higher Maintenance Requirements:
Due to its operating principle, aeroponics systems might require more frequent checks and maintenance to ensure their proper functioning.
2.4.4. Size:
Larger Size, Mostly Placed Outdoors, and Requires a Well-lit Position.
3. Factors to Consider When Choosing a System

Choosing between hydroponics and aeroponics as a planting method is not a straightforward decision. Farmers and gardening enthusiasts need to weigh various factors to determine which system best suits their needs.
3.1. Cost Considerations
3.1.1. Initial Investment:
Both hydroponic and aeroponics systems require a certain initial investment. Typically, the initial cost for aeroponics systems might be higher due to transportation costs from its larger size, the purchase unit price, outdoor water pipe and electrical wire layout, and also depends on the scale and complexity of the chosen system.
3.1.2. Operational Costs:
Beyond the initial costs, considerations should also be made for the costs of water, electricity, nutrient solutions, other maintenance, and external extension accessories. For outdoor planting, the length of different water inlets and the distance of power outlets need to be planned, and some distance for moving pipes should be reserved.
3.2. Space and Location
3.2.1. Available Space Size:
Both hydroponics and aeroponics can be implemented in limited spaces. However, the choice of which system to use also depends on how much space is available. Hydroponics can be chosen for indoors, while aeroponics is mostly outdoors or indoors near windows, and how many plants you wish to cultivate. Is it for one person or a family portion?
3.2.2. Lighting Conditions:
Plants require light for photosynthesis. Consider the natural lighting conditions of your planting area or if additional artificial lighting will be needed. Aeroponics might require additional installations for this, while indoor hydroponics usually come equipped.
3.3. Technical and Maintenance
3.3.1. Technical Difficulty:
Aeroponics is often considered a more technically demanding system, considering factors like water pressure for spraying, angles of the spray heads, etc. Indoor hydroponics, on the other hand, is relatively easier to manage, typically requiring just three steps: plug in, set up, and place seeds.
3.3.2. Maintenance Frequency and Complexity:
While both systems require periodic maintenance, aeroponics might need more frequent checks due to water pressure monitoring, larger cleaning spaces, and more planting holes to inspect, ensuring sprayers and other equipment are functioning correctly.
3.4. Growth Objectives

3.4.1. Types of Plants to Cultivate:
Almost all plants are suitable for hydroponics or aeroponics. However, consider the size of the plants you wish to cultivate and their specific environmental needs. For instance, larger plants might be more suitable for aeroponics, while frequently used fresh herbs might be better for hydroponics.
3.4.2. Expected Yield:
If your goal is to maximize yield, then you might need to consider which system can better meet this requirement. Whether you're looking for a one-time yield or frequent harvesting.
3.5. Environmental Factors
3.5.1. Water Quality:
The quality of water directly affects the health of the plants. Consider if your water source contains any substances that might be harmful to plants. Using pure water with added nutrient solution is recommended, but considering costs, filtered water can also be used.
3.5.2. Climatic Conditions:
Although both hydroponics and aeroponics can be done indoors, if you choose to cultivate outdoors, then local climatic conditions might influence your decision, such as cloudy days or rainy days. In this aspect, hydroponics won't be affected at all.
In light of the above differences, potential buyers need to be clear about what they need and what they want to plant. If someone is new to this, starting with indoor hydroponic equipment will provide a better understanding and learning experience. Once familiar, they can then explore aeroponics.
Other Plant Hydroponic Growing Tips
If you are also interested in other hydroponic plants, please read related articles.
- The Best 11 Easy-To-Grow Vegetables in Hydroponics
- Top 10 Fruits to Grow in Hydroponic Systems
- Hydroponic Herbs: A Beginner's Top 10 List
- How to grow hydroponic cherry tomatoes Indoors: A Detailed Guide
- How to grow cilantro hydroponically indoors: A Beginner’s Guide
- How to grow Hydroponic Bell Peppers indoors: A Detailed Guide
- How to Grow Hydroponic Blueberries Indoors: A Detailed Guide




















Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.